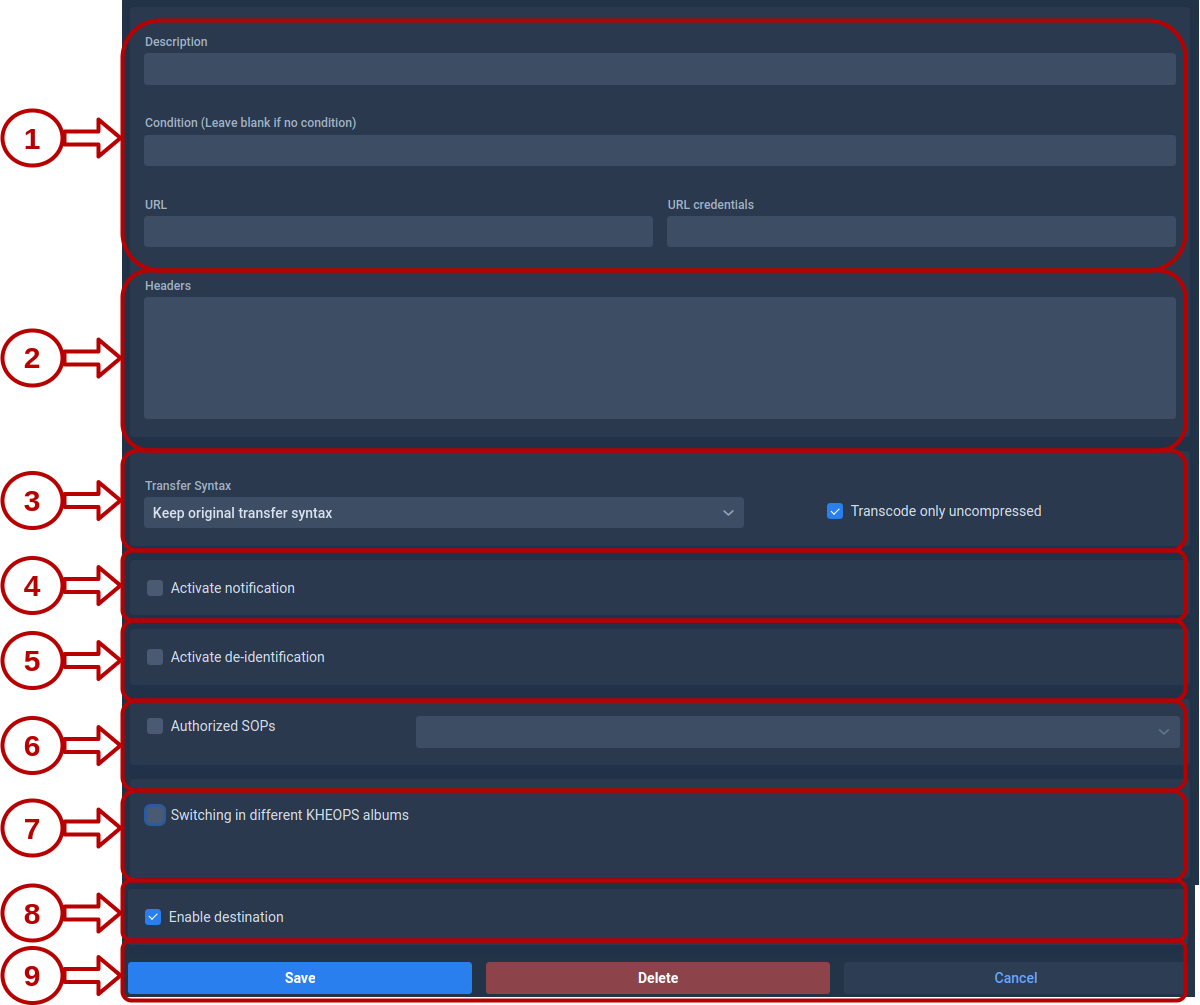
Destinations
This page allows you to configure destinations for your forward nodes. Destinations define where DICOM instances are sent and how they are processed during transfer.
Info
To access this page, first select a forward node from the Gateway page, then click the Destinations tab.
Depending on the protocol used, two types of destinations can be created:
- DICOM Destinations - Traditional DICOM protocol
- STOW Destinations - DICOMWeb (STOW-RS) protocol
DICOM Destination
A DICOM Destination uses the traditional DICOM protocol to forward instances to another DICOM node.
Creating a DICOM Destination
AETitle, Hostname and Port are mandatory when creating a DICOM Destination.
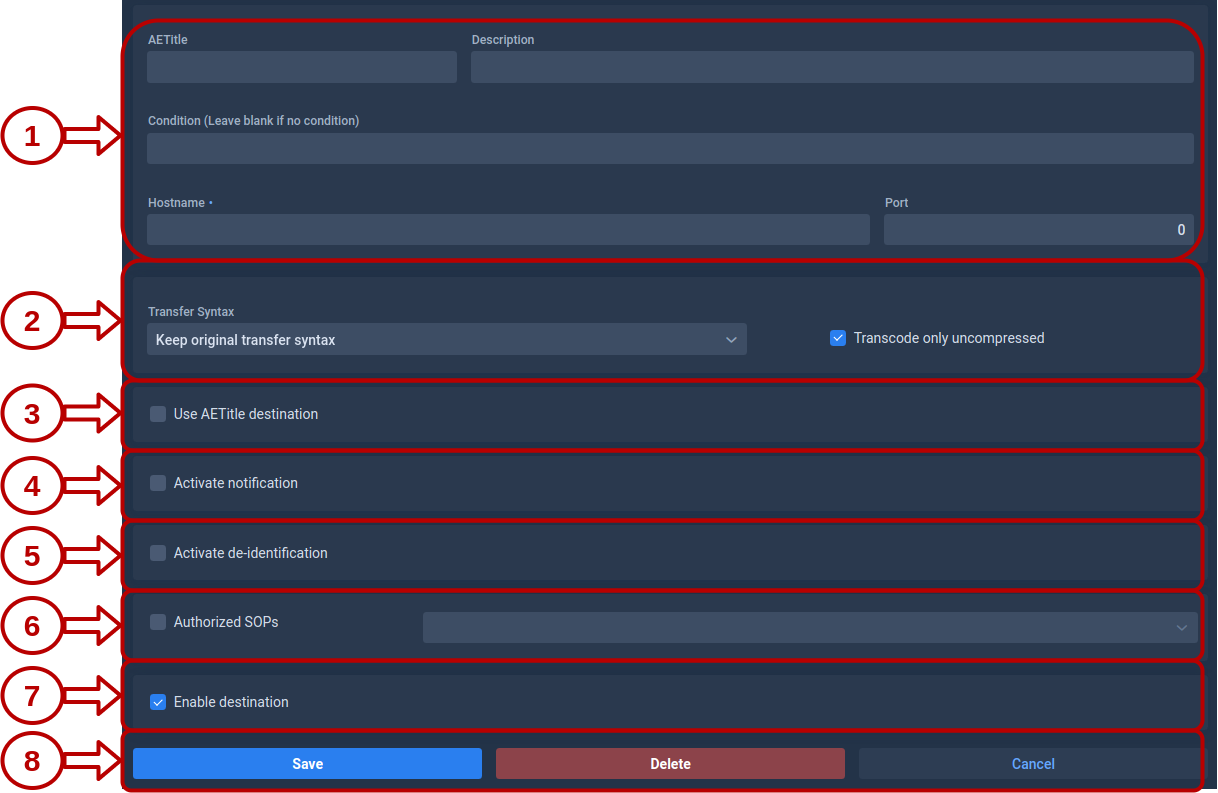
Configuration Options
1. Destination Parameters
These fields define where Karnak should send the DICOM instances.
- AETitle: The Application Entity Title that identifies the destination DICOM node.
- Hostname: The IP address or hostname of the destination server.
- Port: The network port used by the destination DICOM service (must be between 1 and 65535).
- Condition: An optional field that can contain an expression. If the condition is met, the destination will be activated. See Conditions for more details.
2. Transfer Syntax
This field defines the transfer syntax used when sending DICOM instances to this destination. The transfer syntax determines the encoding and compression format of the DICOM data.
It is recommended to choose “Keep original transfer syntax” unless you have specific requirements for compression or compatibility with the destination system.
When selecting a specific transfer syntax, ensure that the destination system supports it to avoid decompression or compatibility issues. It is also recommended to check “Transcode only uncompressed” when selecting lossy syntaxes to avoid re-compressing already compressed data.
Info
Transcoding may increase processing time and resource usage, especially for large datasets. Use it judiciously based on your workflow needs.
3. Use AETitle Destination
When this option is checked, use the destination AETitle as the calling AETitle instead of the Forward Node AETitle during the DICOM association.
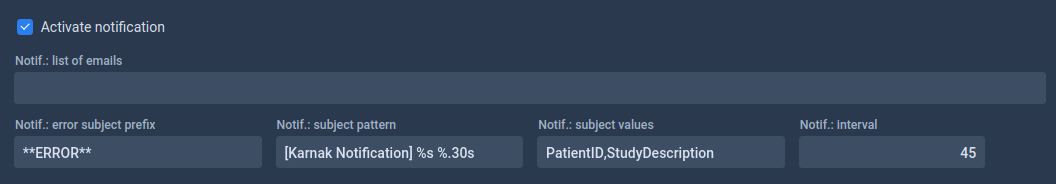
4. Notifications
Enable email notifications to receive automatic summaries of forwarded instances, including success and error reports.
Configuration fields:
| Field | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| List of emails | Comma-separated list of recipient email addresses | None |
| Error subject prefix | Prefix added to email subjects when an error occurs | **ERROR** |
| Rejection subject prefix | Prefix added when an instance is rejected due to filters or criteria | **REJECTED** |
| Subject pattern | Email subject template using Java String Format | [Karnak Notification] %s %.30s |
| Subject values | DICOM attributes to inject into the subject pattern (PatientID, StudyDescription, StudyDate, StudyInstanceUID) | PatientID,StudyDescription |
| Interval | Time in seconds to wait before sending notification (aggregates multiple instances) | 45 |
Info
The interval setting helps reduce email volume by aggregating notifications. All instances received within the specified interval are summarized in a single email.
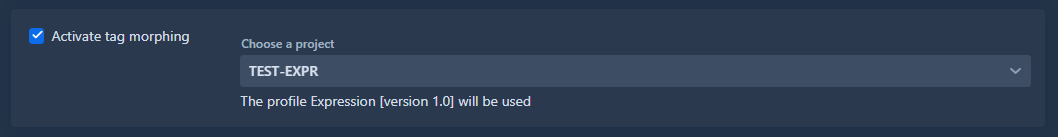
5. Tag Morphing
Tag morphing allows you to modify specific DICOM tag values defined in a profile. With this mode, it is not mandatory to de-identify patient information like in De-identification mode.
Prerequisites:
- A project must be created first
- The project must have an associated profile
Configuration:
- Select the project from the dropdown
- The applied profile and its version are displayed below the selection
Info
Activate tag morphing and Activate de-identification are mutually exclusive options. Only one can be active at a time.
6. De-identification
De-identification removes or replaces patient-identifying information in DICOM instances according to configurable rules and profiles. It is not possible to preserve the patient identity in the profile when this option is activated.
Info
Activate de-identification and Activate tag morphing are mutually exclusive options. Only one can be active at a time.
Prerequisites:
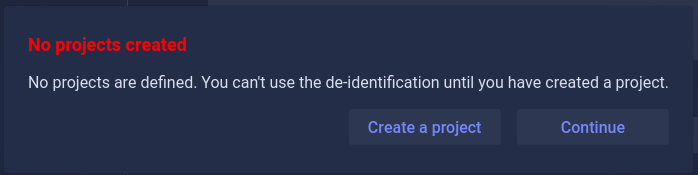
To activate de-identification, you must create a project first.
If no project exists:
A popup will appear with two options, either create a project or continue without activating de-identification.
If a project exists:
Configure de-identification as shown below:
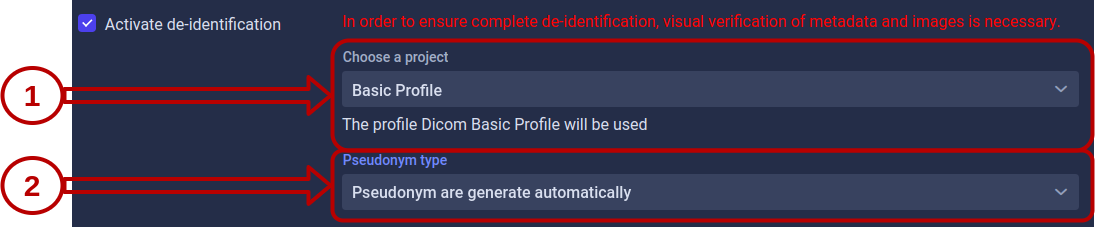
Project Selection
Select the project that defines the de-identification profile to apply. The profile name and version are displayed below the selection.
Each project is associated with:
- A de-identification profile
- A secret key used for pseudonymization and UID generation
See the Projects page for more information about project configuration.
Pseudonym Type
Pseudonyms replace patient identifiers while maintaining the ability to link de-identified data back to the original patient (when necessary and authorized).
Choose how Karnak should retrieve or generate pseudonyms:
| Type | Description | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Pseudonym is already stored in KARNAK | Queries the internal pseudonym cache | When using External Pseudonym |
| Pseudonym is in a DICOM tag | Extracts pseudonym from a specified DICOM tag | When pseudonyms are pre-populated in DICOM data |
| Pseudonym from external API | Retrieves pseudonym via API call | When using external pseudonymization services |
Pseudonym is already stored in KARNAK
This option queries the pseudonym stored in the internal cache as explained in External Pseudonym.
Behavior:
- Karnak queries its internal cache using the Patient ID and Issuer of Patient ID
- If a pseudonym is found, it is used for de-identification
- If no pseudonym is returned, the transfer of the DICOM instance is aborted. Ensure pseudonyms are correctly populated in External Pseudonym.
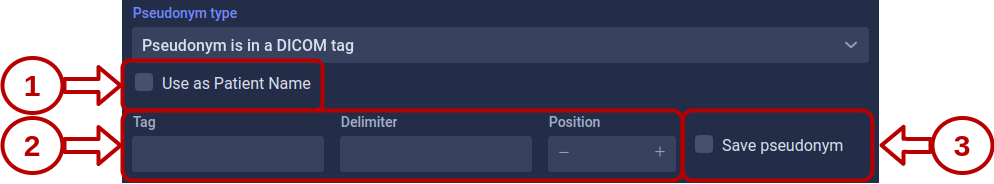
Pseudonym is in a DICOM tag
This option retrieves the pseudonym from a specified DICOM tag within the instance itself.
Required configuration:
- Tag number: The DICOM tag containing the pseudonym (e.g., Clinical Trial Subject ID
(0012,0040))
Optional configuration:
- Delimiter: Character used to split the tag value
- Position: Which part to use after splitting (zero-based index)
Example:
If tag (0012,0040) contains "SITE01-PSN12345" and you set:
- Delimiter:
- - Position:
1
The pseudonym will be "PSN12345".
If no delimiter and position are specified, the entire tag value is used as the pseudonym.
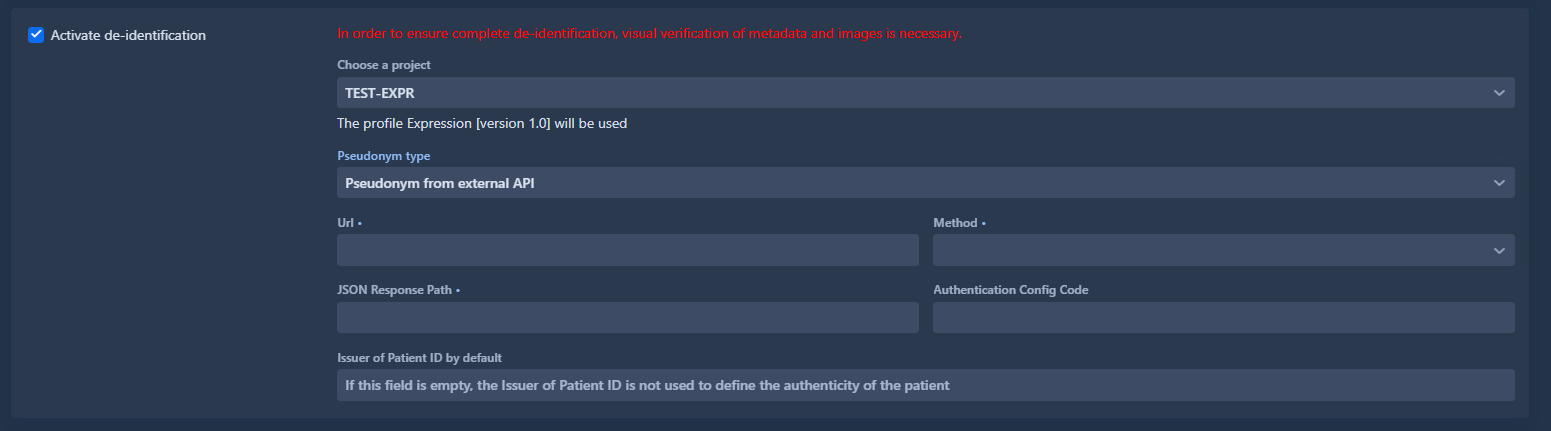
Pseudonym from external API
This option makes an API call to retrieve the pseudonym from an external service.
The detailed usage of all the fields is explained in the API Actions page. The behavior is identical to profile API actions.
You can reference an Authentication Configuration to securely manage API credentials for OAuth 2.0.
Issuer of Patient ID by Default
This field provides a default value for the Issuer of Patient ID when it’s not present in the DICOM instance.
Usage:
This value is used when retrieving the pseudonym using the External Pseudonym cache. The pseudonym is queried based on:
- Patient ID (from DICOM tag
0010,0020) - Issuer of Patient ID (from DICOM tag
0010,0021or this default value)
The combination of Patient ID and Issuer ensures unique patient identification across different healthcare systems.
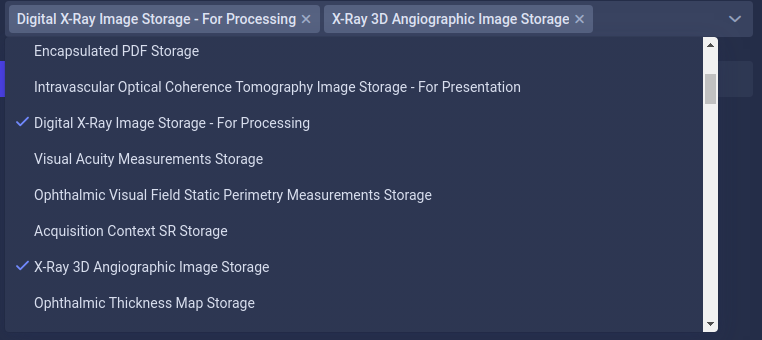
7. Authorized SOPs
Filter which DICOM instance types (SOP Classes) are forwarded to this destination.
Configuration:
- Enabled: Only instances matching the specified SOP Classes are transferred
- Disabled: All SOP Classes are transferred without restriction
8. Enable the Destination
This toggle allows you to temporarily disable a destination without deleting it. The state is also visible in the destination list with a green (enabled) or red (disabled) indicator.
Use this feature to:
- Temporarily pause forwarding during maintenance
- Test configurations without affecting production destinations
- Keep backup destination configurations ready but inactive
9. Action Buttons
Three actions are available to manage the destination:
| Button | Description |
|---|---|
| Save | Saves all changes made to the destination configuration |
| Delete | Permanently deletes the selected destination |
| Cancel | Reverts all unsaved changes to the last saved state |
Warning
Deleting a destination cannot be undone. All configuration settings will be permanently removed.
Creating a STOW Destination
The URL is required for STOW Destination creation. Most configuration options are identical to DICOM Destinations. Only the differences are detailed below.
Configuration Differences
1. Destination Parameters
URL: The DICOMweb STOW-RS endpoint where DICOM instances will be sent (e.g., https://pacs.example.com/dicomweb/studies).
Condition: An optional expression that activates the destination when met. See Conditions for more details.
HTTP Headers
The Headers field contains HTTP headers added to each STOW-RS request.
Format: Headers are defined using XML-style key-value tags as shown below:
Generate Authorization Header
Click the Generate Authorization Header button to automatically generate properly formatted authentication headers.
Warning
If a header with <key>Authorization</key> already exists, an error will be displayed. The generator will append to existing headers if they don’t conflict.
Supported Authorization Types:
Basic Authentication
Use for simple username/password authentication:
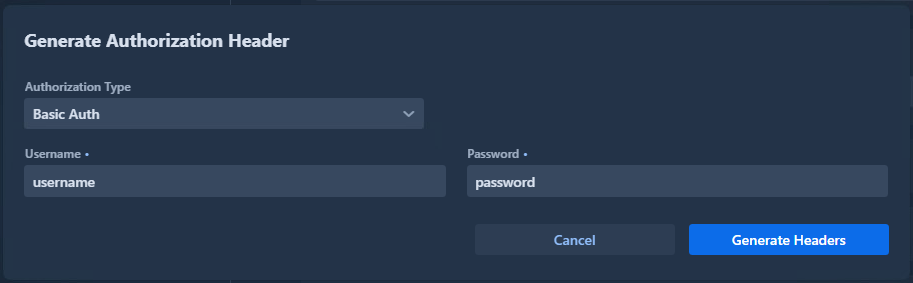
Generated headers:
The username and password are Base64-encoded automatically.
OAuth 2.0
Use for token-based authentication:
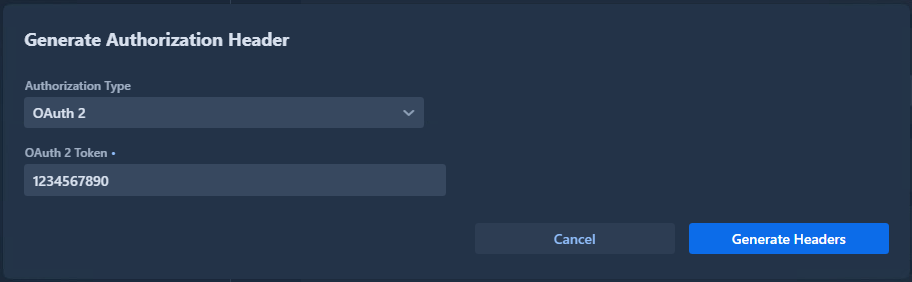
Generated headers:
2. Switching to different Kheops albums
If the destination is a Kheops endpoint, it is possible to configure multiple albums by selecting the option “Switching in different KHEOPS albums”.
Explanations for configuring Kheops-related parameters can be found in the Kheops section.